
If you put the energy back in, then the nucleus would fly apart.Īnyway, back to carbon-13. Because of this energy being released, a carbon-12 nucleus is more stable than six protons and six neutrons are by themselves. So why does C-12 have less mass than the sum of its components? The extra mass is converted to energy (E = mc2), which is released. If you add the masses of six protons and six neutrons, you get 12.09. The actual mass of a proton is about 1.007 amu, and the mass of a neutron is about 1.008 amu. Theoretically, this would mean that each proton and each neutron has a mass of one amu, but this turns out not to be so. 1999‑2023 - All Rights Reserved.It's because of something called binding energy.Ĭarbon-12 has a mass of 12 amu by definition. Retrieved from Ĭopyright © Israel Science and Technology Directory. "Sortable list of elements of the Periodic Table".
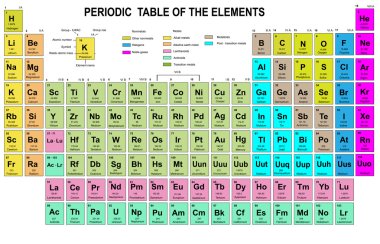
Multilingual Dictionary and Etymology of the Periodic Table Elements.Atomic Reference Data for Electronic Structure Calculations.List of Periodic Table Elements in Hebrew.Other resources related to the Periodic Table For these elements, the weight value represents the mass number of the longest-lived isotope of the element.Įlectron configuration: See next page for explanation of electron configuration of atoms. The elements marked with an asterisk have no stable nuclides. The values shown here are based on the IUPAC Commission determinations ( Pure Appl. For relative abundances of isotopes in nature, see reference on Atomic Weights and Isotopic Compositions.Ītomic weight: Atomic weight values represent weighted average of the masses of all naturally occurring isotopes of an element. The abundance of each isotope depends on the source of materials. For example, the two common isotopes of carbon, 12C and 13C, have 6 and 7 neutrons, respectively. Elements have more than one isotope with varying numbers of neutrons. The isotope of an element is defined by the sum of the number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus. Isotope: Atoms of the same element with the same atomic number, but a different number of neutrons. Thus, each proton and neutron has a mass of about 1 amu. This isotope of carbon has 6 protons and 6 neutrons. Atomic mass is measured in Atomic Mass Units (amu), which are scaled relative to carbon, 12C, that is taken as a standard element with an atomic mass of 12. Each element is uniquely defined by its atomic number.Ītomic mass: The mass of an atom is primarily determined by the number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus.
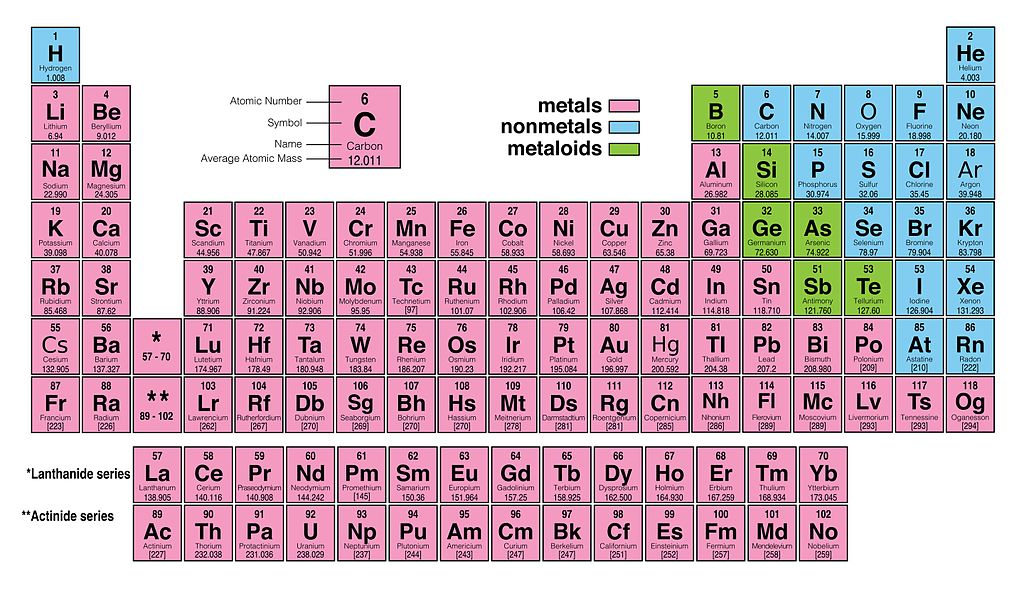
Boiling pointĪtomic number: The number of protons in an atom. For the Year of Discovery of elements see the list with the English and Hebrew names.

For these elements, the weight value shown represents the mass number of the longest-lived isotope of the element. The elements marked with an asterisk (in the 2nd column) have no stable nuclides.Lanthanoids and Actinoids are numbered as 101 and 102 to separate them in sorting by group. Group: There are only 18 groups in the periodic table that constitute the columns of the table.Elemental compositions of crustal rocks differ between different localities ( see article). Earth crust composition average values are from a report by F.In a sorted list, these elements are shown before other elements that have boiling points >0☌. The density of elements with boiling points below 0☌ is given in g/l.List of Periodic Table elements sorted by → Atomic number No.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
